Best Foods for Managing Blood Sugar Levels and Combating Diabetes
Oct. 2, 2023 #Diabetes
Introduction
Diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by elevated blood sugar levels, impacting the body's ability to regulate insulin effectively. This metabolic disorder comes in two main types: Type 1, where the body doesn't produce insulin, and Type 2, where the body doesn't use insulin properly. Both types can lead to serious complications if not managed effectively. One crucial aspect of diabetes management is maintaining stable blood sugar levels, and a key way to achieve this is through a well-balanced and diabetes-friendly diet.
Understanding Diabetes: Causes and Symptoms
Diabetes develops when the pancreas either produces insufficient insulin or when the body cannot effectively use the insulin it produces. In Type 1 diabetes, the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. This results in little to no insulin production. In Type 2 diabetes, the body becomes resistant to insulin, and over time, the pancreas can't keep up with the demand, leading to inadequate insulin levels.
Common symptoms of diabetes include excessive thirst, frequent urination, unexplained weight loss, increased hunger, fatigue and slow-healing wounds. It's crucial to recognize these signs and seek medical attention for early diagnosis and management.
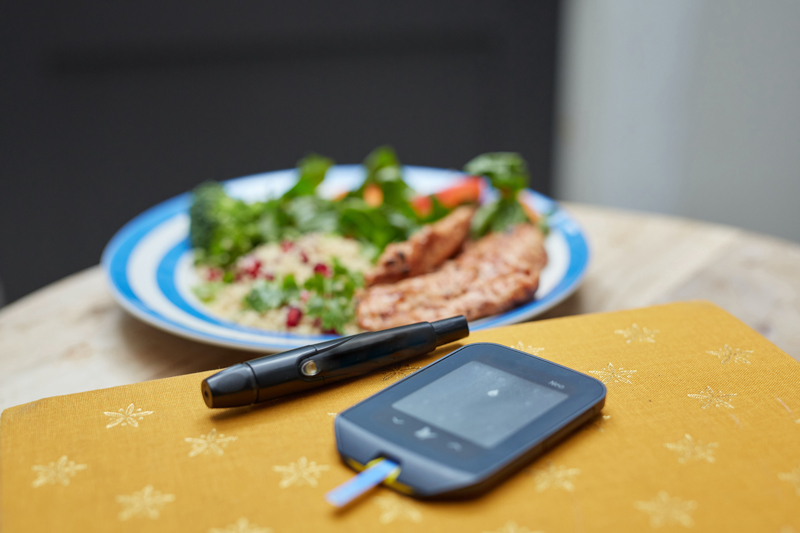
Best Foods for Blood Sugar Control
Maintaining stable blood sugar levels is essential for individuals with diabetes. Adopting a diet rich in nutrient-dense, low-glycemic foods can help achieve this goal. Here are some of the best foods to include in a diabetes-friendly diet:
1. Non-Starchy Vegetables:
Include a variety of non-starchy vegetables like leafy greens, broccoli, cauliflower, bell peppers and zucchini. These veggies are low in carbohydrates and high in fiber, promoting satiety without causing significant spikes in blood sugar.
2. Whole Grains:
Opt for whole grains such as quinoa, brown rice and oats over refined grains. Whole grains provide a steady release of glucose, helping to manage blood sugar levels.
3. Lean Proteins:
Choose lean protein sources like poultry, fish, tofu, legumes and eggs. Protein-rich foods help with satiety and do not substantially impact blood sugar levels.
4. Healthy Fats:
Incorporate sources of healthy fats such as avocados, nuts, seeds and olive oil. Healthy fats contribute to a well-rounded diet and can help stabilize blood sugar.
5. Berries:
Berries, such as blueberries, strawberries and raspberries, are rich in antioxidants and fiber. Their natural sweetness makes them a delicious and blood sugar-friendly option.
6. Greek Yogurt:
Greek yogurt is a protein-packed dairy option with probiotics that support gut health. You should choose plain, unsweetened varieties to avoid added sugars.
7. Cinnamon:
Cinnamon may have beneficial effects on blood sugar and insulin sensitivity. Sprinkle cinnamon on foods or add it to beverages for flavor without added sugars.
8. Legumes:
Legumes like lentils, chickpeas and black beans are excellent sources of protein and fiber. They have a minimal impact on blood sugar and provide long-lasting energy.
9. Sweet Potatoes:
Sweet potatoes are a nutritious, fiber-rich alternative to regular potatoes. They offer a good dose of vitamins and minerals while being lower on the glycemic index.
10. Fatty Fish:
- Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel and sardines are high in omega-3 fatty acids.
- These fats have been linked to improved insulin sensitivity and heart health.
Daily Diabetes Management Through Diet
Beyond individual food choices, the timing and composition of meals also play a vital role in blood sugar management. Consider the following tips for daily diabetes management:
1. Portion Control:
Monitor portion sizes to avoid overeating, which can lead to blood sugar spikes. Use measuring tools or visual cues to gauge appropriate portions.
2. Balanced Meals:
Aim for balanced meals that include a combination of protein, fiber and healthy fats. This combination helps slow down the absorption of glucose and keeps blood sugar levels stable.
3. Regular Meal Timing:
Establish a consistent meal schedule with regular intervals between meals. This routine helps the body manage blood sugar more effectively.
4. Hydration:
Stay hydrated with water throughout the day. Limit sugary beverages and opt for water, herbal tea, or infused water.
5. Mindful Eating:
Practice mindful eating by savoring each bite and paying attention to hunger and fullness cues. This approach can prevent overeating and promote a healthier relationship with food.
6. Carb Monitoring:
Monitor carbohydrate intake and choose complex carbs over simple sugars. Distribute carbs evenly throughout meals to avoid sudden spikes.
7. Regular Monitoring:
Regularly monitor blood sugar levels as advised by healthcare professionals. This helps track the effectiveness of dietary choices and medication management.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a well-planned and balanced diet is a cornerstone of effective diabetes management. By incorporating nutrient-dense, low-glycemic foods and adopting healthy eating habits, individuals with diabetes can better control blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of complications. It's essential to work closely with healthcare professionals, including registered dietitians, to create a personalized and sustainable dietary plan that aligns with individual health needs and preferences. Making informed food choices is not just a strategy for managing diabetes but a pathway to overall well-being and vitality.










COMMENTS